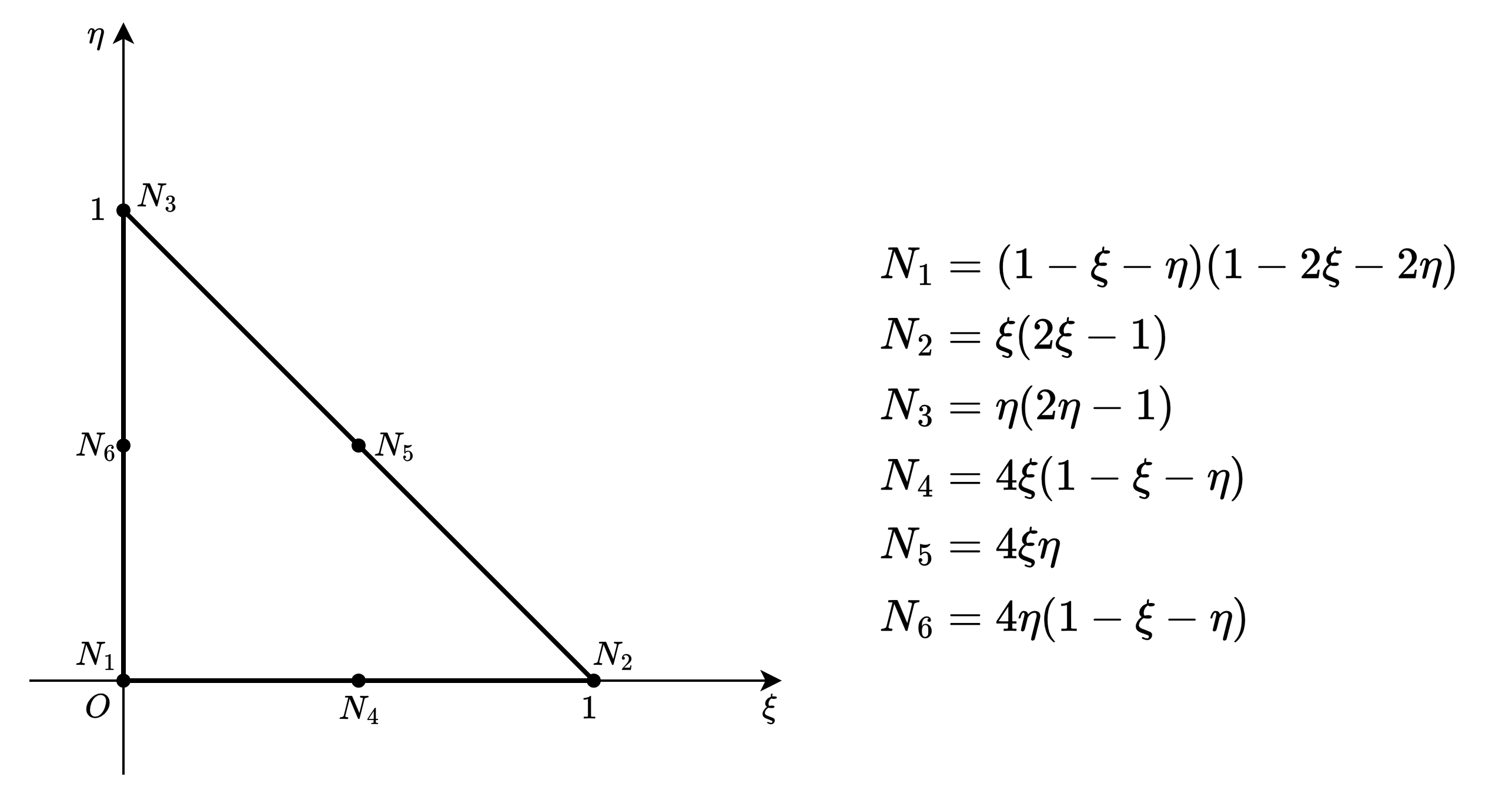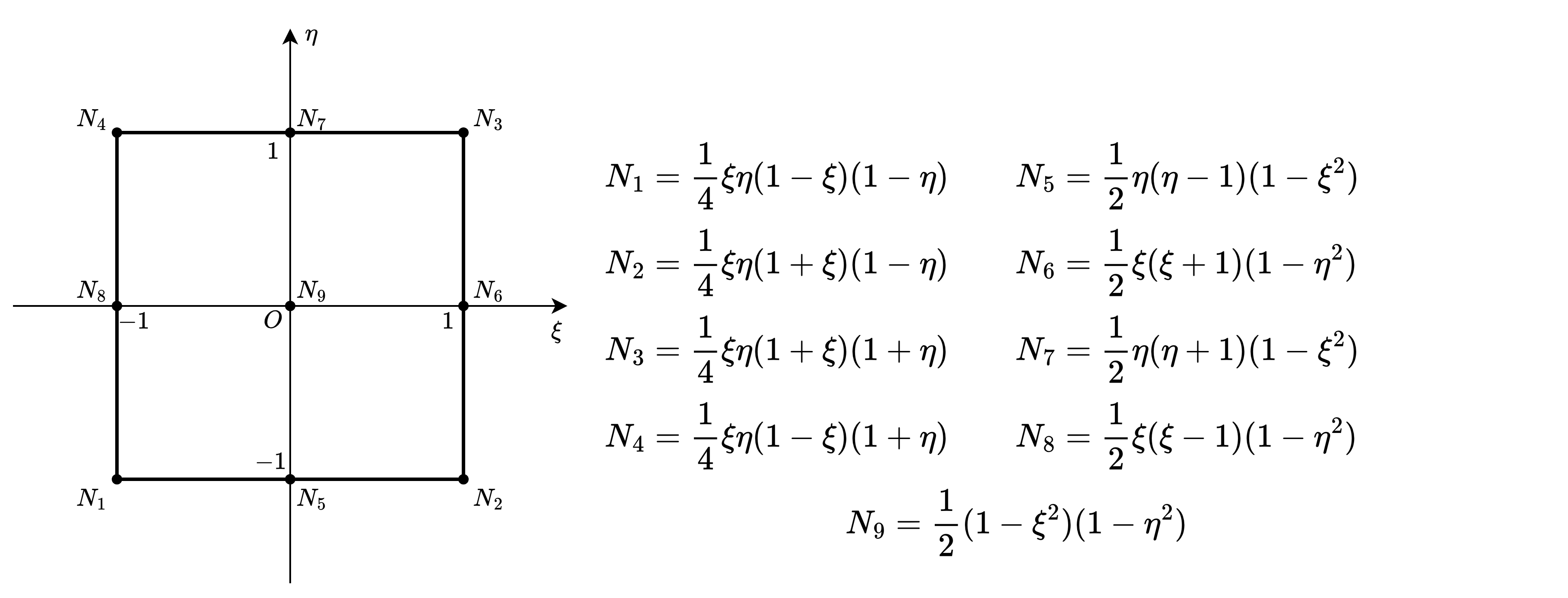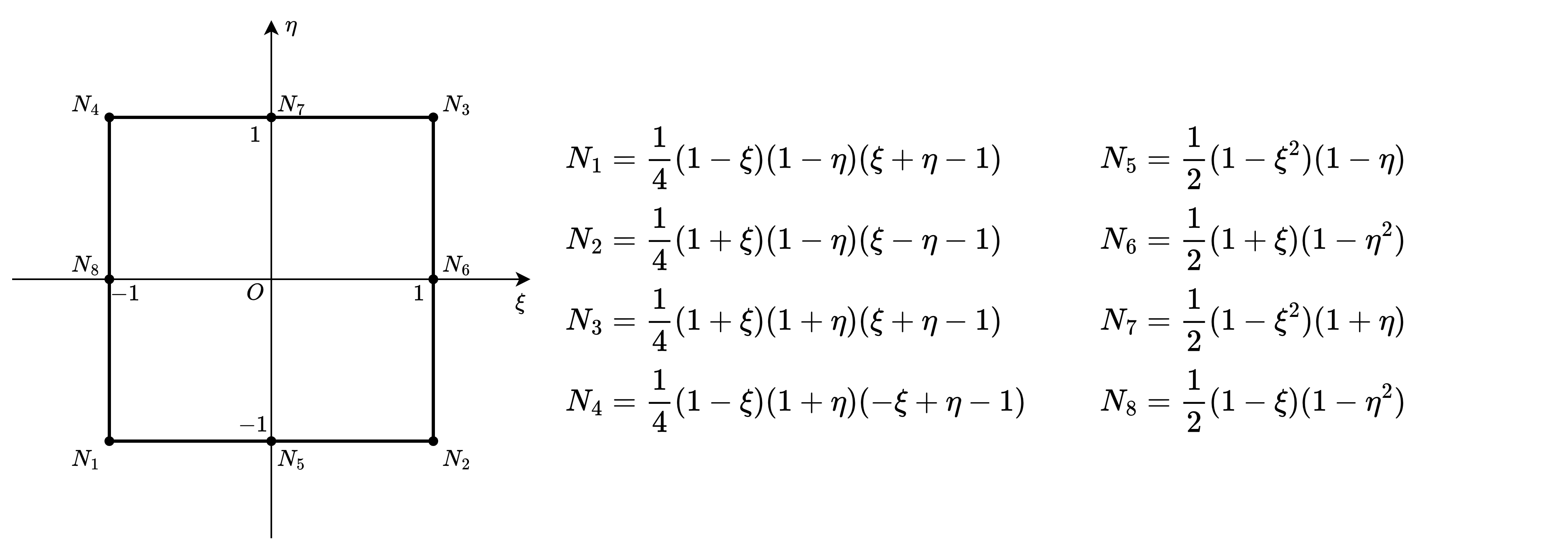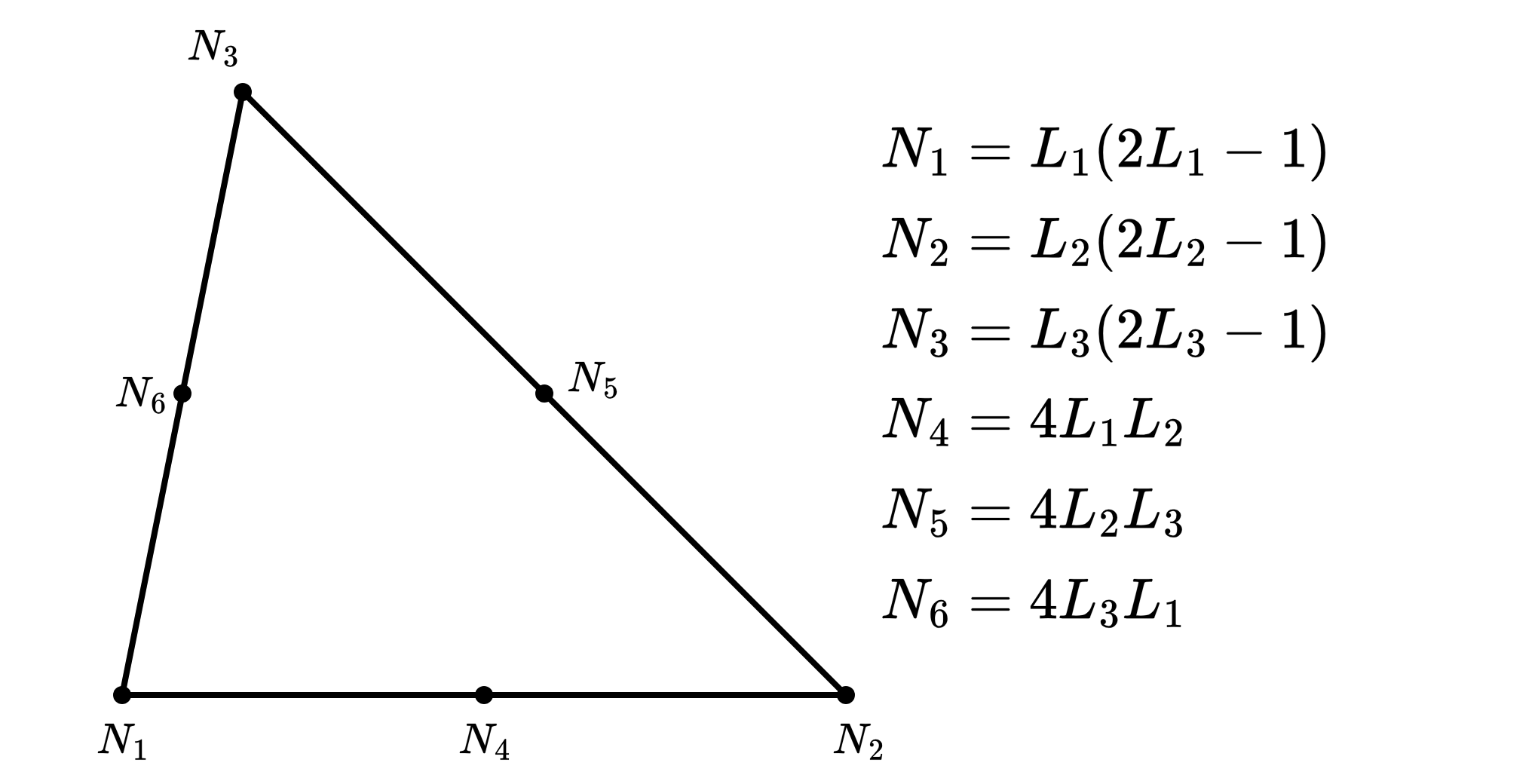import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
# 一维单元形函数
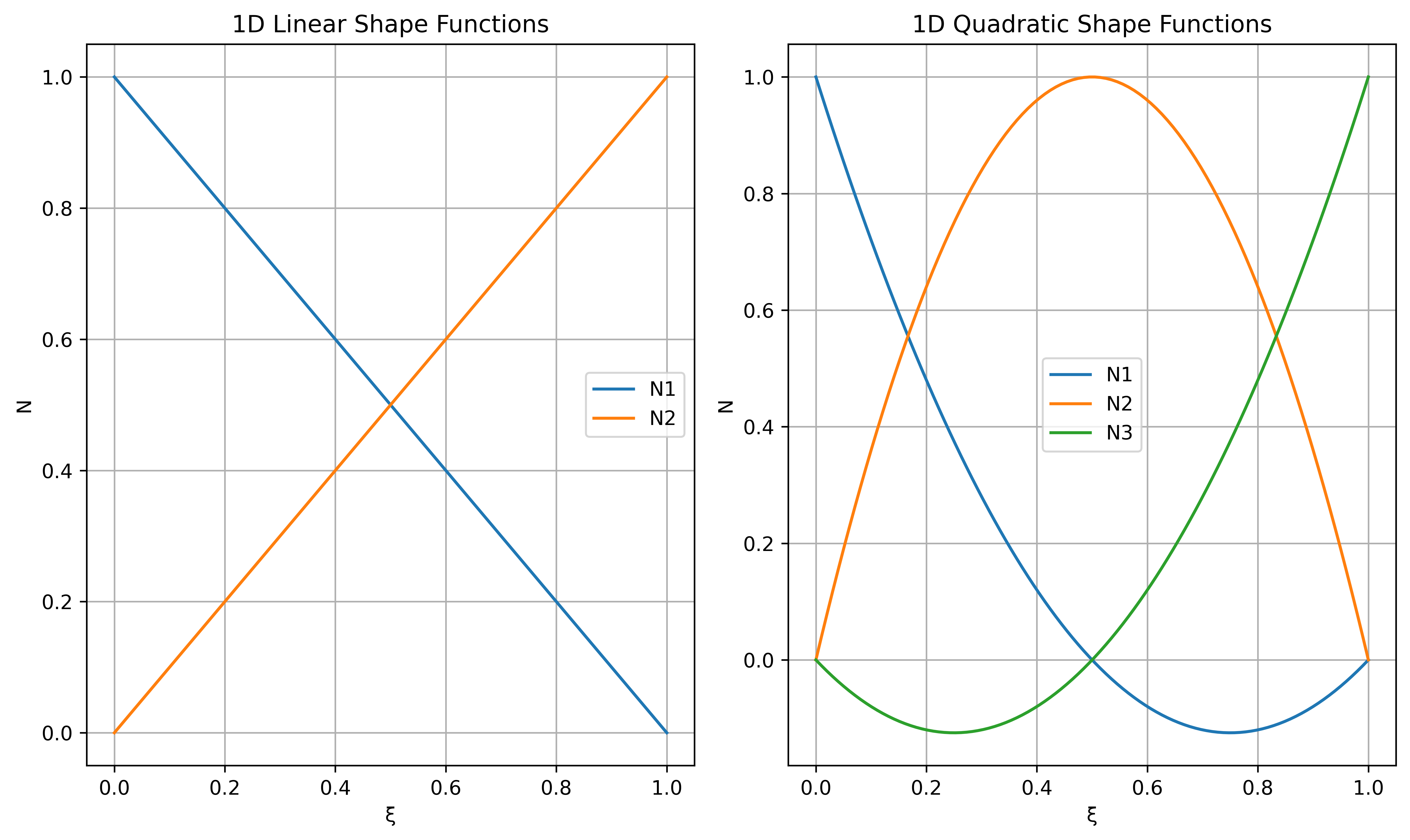
def plot_1d_shape_functions():
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
# 一次形函数
N1_1 = 1 - x
N2_1 = x
# 二次形函数
N1_2 = (1 - x) * (1 - 2 * x)
N2_2 = 4 * x * (1 - x)
N3_2 = x * (2 * x - 1)
# 节点位置
nodes_linear = [0, 1]
nodes_quadratic = [0, 0.5, 1]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6), dpi=600)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(x, N1_1, label='N1', color='#1f77b4')
plt.plot(x, N2_1, label='N2', color='#ff7f0e')
# 标注一次形函数的节点
# plt.scatter([0,1],[1,0], color='#1f77b4')
# plt.scatter([0,1],[0,1], color='#ff7f0e')
plt.title('1D Linear Shape Functions')
plt.xlabel('ξ')
plt.ylabel('N')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(x, N1_2, label='N1', color='#1f77b4')
plt.plot(x, N2_2, label='N2', color='#ff7f0e')
plt.plot(x, N3_2, label='N3', color='#2ca02c')
# 标注二次形函数的节点
# plt.scatter([0,0.5,1],[1,0.5,0], color='#1f77b4')
# plt.scatter([0,0.5,1],[0,1,0], color='#ff7f0e')
# plt.scatter([0,0.5,1],[0,0,1], color='#2ca02c')
plt.title('1D Quadratic Shape Functions')
plt.xlabel('ξ')
plt.ylabel('N')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 三角形单元形函数
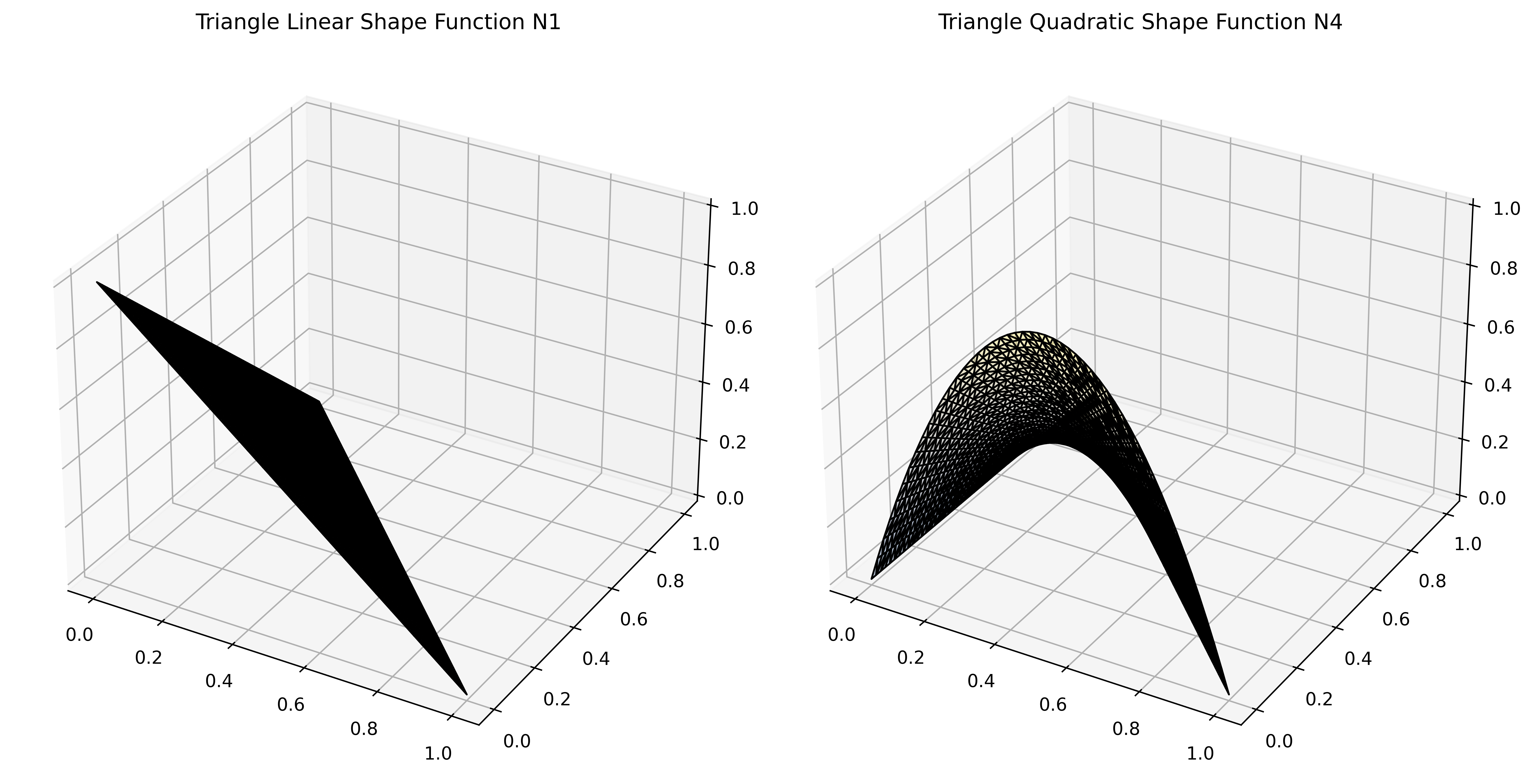
def plot_triangle_shape_functions():
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6), dpi=600)
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 50)
y = np.linspace(0, 1, 50)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
mask = X + Y <= 1
X = X[mask]
Y = Y[mask]
# 一次形函数
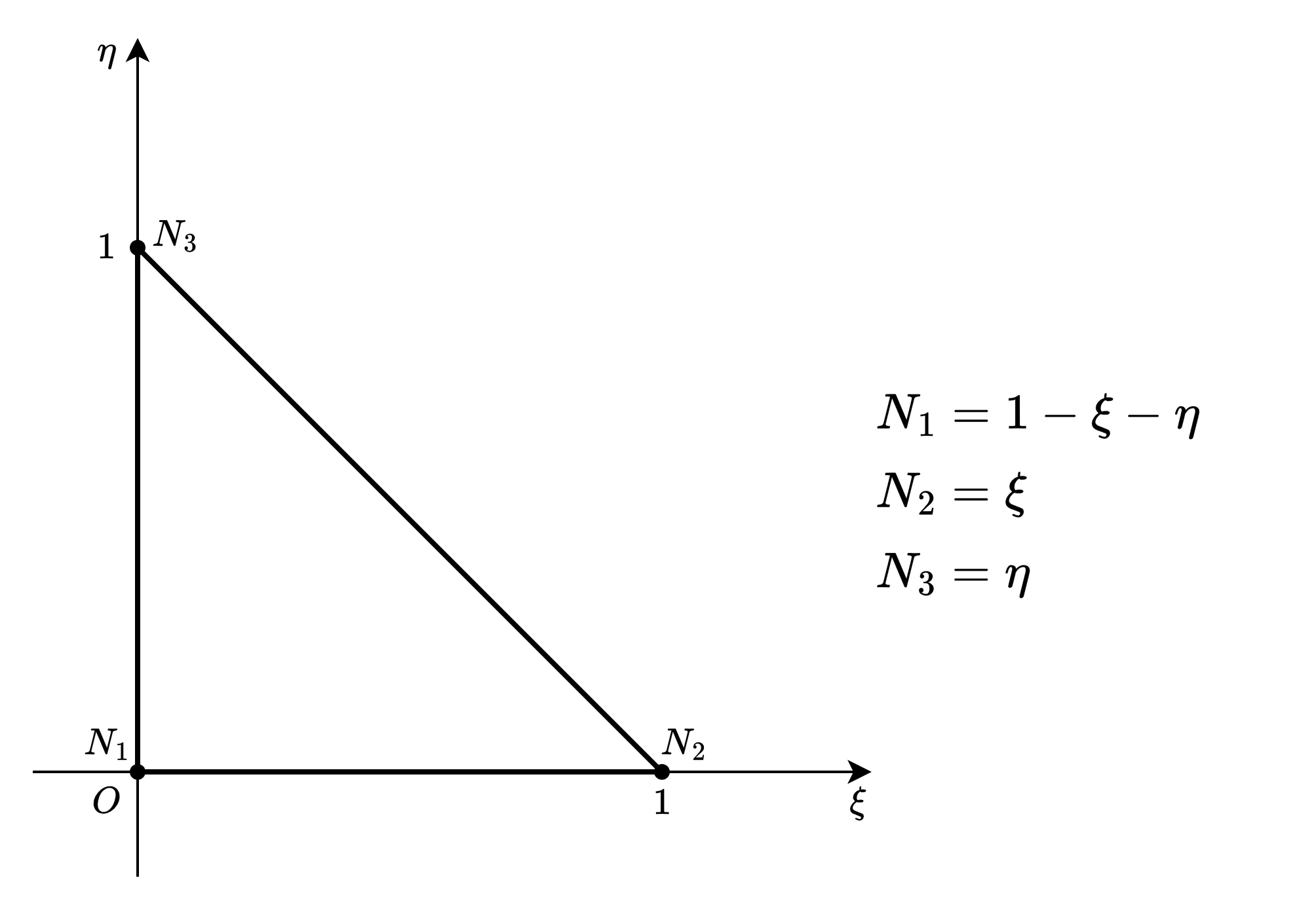
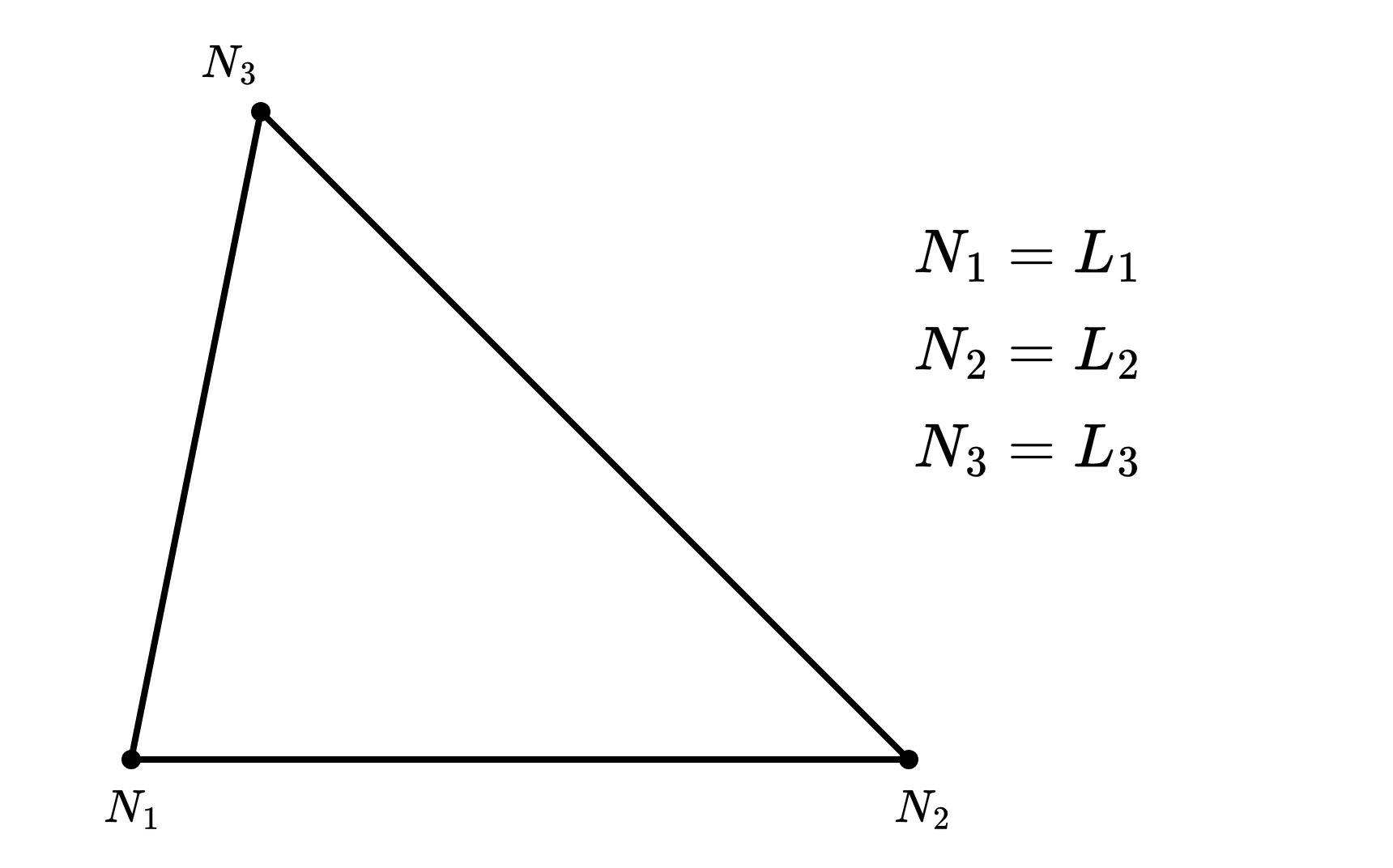
N1_1 = 1 - X - Y
N2_1 = X
N3_1 = Y
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121, projection='3d')
ax1.plot_trisurf(X, Y, N1_1, cmap='cividis', edgecolor='k', alpha=0.3)
ax1.set_title('Triangle Linear Shape Function N1')
# 二次形函数
N1_2 = (1 - X - Y) * (1 - 2 * (X + Y))
N2_2 = X * (2 * X - 1)
N3_2 = Y * (2 * Y - 1)
N4_2 = 4 * X * (1 - X - Y)
N5_2 = 4 * X * Y
N6_2 = 4 * Y * (1 - X - Y)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection='3d')
ax2.plot_trisurf(X, Y, N4_2, cmap='cividis', edgecolor='k', alpha=0.3)
ax2.set_title('Triangle Quadratic Shape Function N4')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 四边形单元形函数
def plot_quadrilateral_shape_functions():
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6), dpi=600)
xi = np.linspace(-1, 1, 50)
eta = np.linspace(-1, 1, 50)
XI, ETA = np.meshgrid(xi, eta)
# 一次形函数
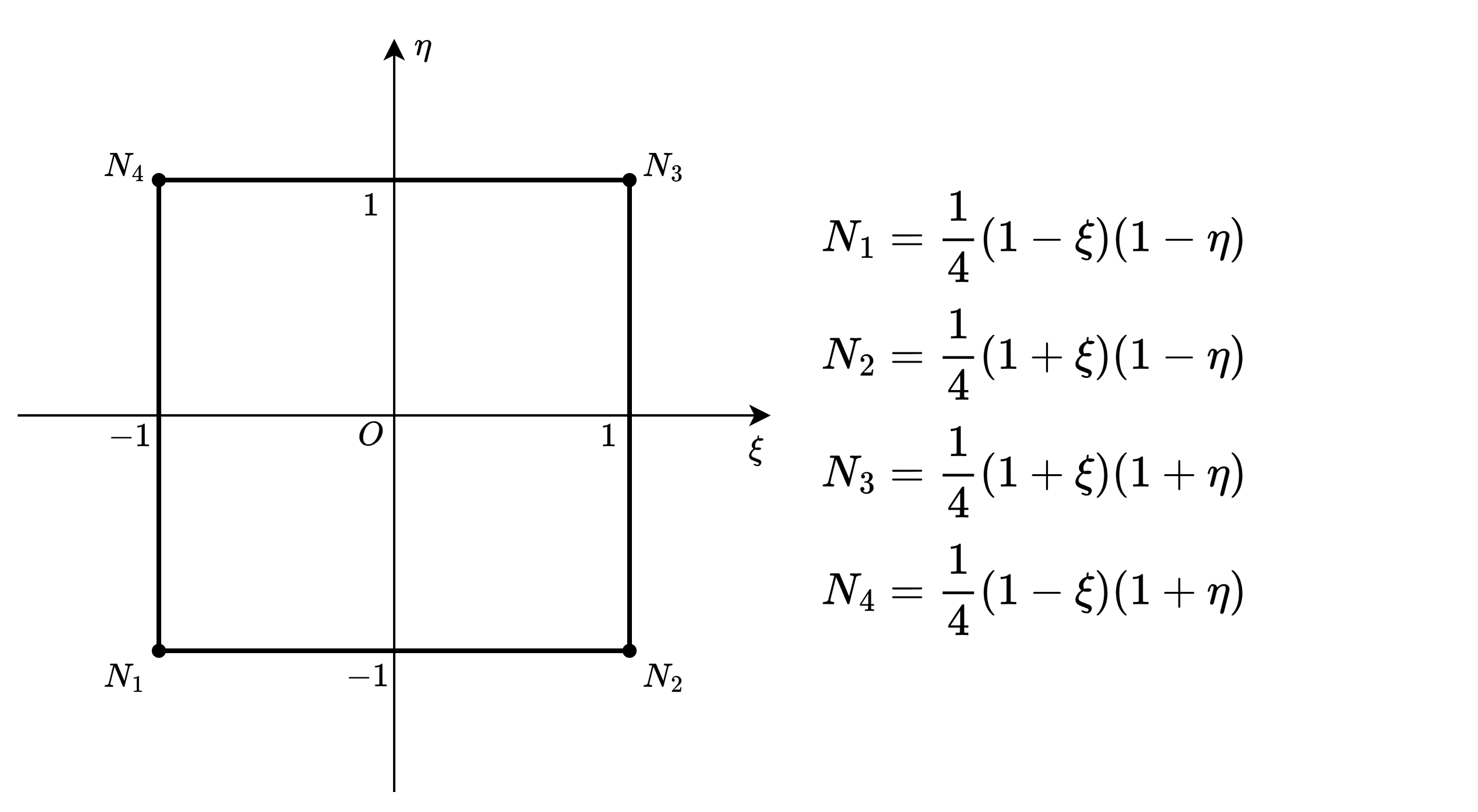
N1_1 = 0.25 * (1 - XI) * (1 - ETA)
N2_1 = 0.25 * (1 + XI) * (1 - ETA)
N3_1 = 0.25 * (1 + XI) * (1 + ETA)
N4_1 = 0.25 * (1 - XI) * (1 + ETA)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121, projection='3d')
ax1.plot_surface(XI, ETA, N1_1, cmap='cividis', edgecolor='k', alpha=0.3)
ax1.set_title('Quadrilateral Linear Shape Function N1')
# 二次形函数
N1_2 = 0.25 * XI * ETA * (1 - XI) * (1 - ETA)
N2_2 = 0.25 * XI * ETA * (1 + XI) * (1 - ETA)
N3_2 = 0.25 * XI * ETA * (1 + XI) * (1 + ETA)
N4_2 = 0.25 * XI * ETA * (1 - XI) * (1 + ETA)
N5_2 = 0.50 * ETA * (ETA - 1) * (1 - XI**2)
N6_2 = 0.50 * XI * (XI + 1) * (1 - ETA**2)
N7_2 = 0.50 * ETA * (ETA + 1) * (1 - XI**2)
N8_2 = 0.50 * XI * (XI - 1) * (1 - ETA**2)
N9_2 = 0.50 * (1 - XI**2) * (1 - ETA**2)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection='3d')
ax2.plot_surface(XI, ETA, N5_2, cmap='cividis', edgecolor='k', alpha=0.3)
ax2.set_title('Quadrilateral Quadratic Shape Function N2')
# 调整视角
ax2.view_init(elev=30, azim=-60) # 设置仰角为 45 度,方位角为 30 度
# 去除三维面板背景(可选)
ax1.grid(False)
ax2.grid(False)
for ax in [ax1, ax2]:
ax.xaxis.pane.set_edgecolor('w')
ax.yaxis.pane.set_edgecolor('w')
ax.zaxis.pane.set_edgecolor('w')
ax.xaxis.pane.set_facecolor((1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0)) # 透明
ax.yaxis.pane.set_facecolor((1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0))
ax.zaxis.pane.set_facecolor((1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 主函数运行
if __name__ == "__main__":
plot_1d_shape_functions()
plot_triangle_shape_functions()
plot_quadrilateral_shape_functions()